
The reason for such a specific cycling pattern of NREM and REM sleep across the night is unknown. The average length of the first NREM-REM sleep cycle is between 70 and 100 minutes the average length of the second and later cycles is about 90 to 120 minutes. During a typical night, N3 sleep occupies less time in the second cycle than the first and may disappear altogether from later cycles. Most slow-wave NREM sleep occurs in the first part of the night REM sleep episodes, the first of which may last only one to five minutes, generally become longer through the night. NREM sleep and REM sleep continue to alternate through the night in a cyclical fashion. REM sleep comprises about 20 to 25 percent of total sleep in typical healthy adults. Typically, a 5- to 10-minute period of N2 precedes the initial REM sleep episode.
#Stages of sleep eeg series#
Thomas Scammell describes the cycles of REM and NREM sleep that occur throughout the night.įollowing the N3 stage of sleep, a series of body movements usually signals an "ascent" to lighter NREM sleep stages.

As NREM sleep progresses, the brain becomes less responsive to external stimuli, and it becomes increasingly difficult to awaken an individual from sleep.ĭr. This stage, which generally lasts 20 to 40 minutes, is referred to as "slow-wave," " delta," or "deep" sleep. As N2 sleep progresses, there is a gradual appearance of the high-voltage, slow-wave activity characteristic of N3, the third stage of NREM sleep.
The second stage, or N2, which is signaled by sleep spindles and/or K complexes in the EEG recording, comes next and generally lasts 10 to 25 minutes. This first period of N1 typically lasts just one to seven minutes.
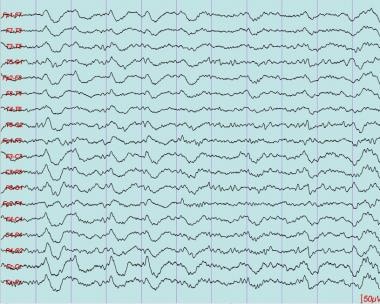
The transition from wakefulness to N1 occurs seconds to minutes after the start of the slow eye movements seen when a person first begins to nod off. The pattern of clear rhythmic alpha activity associated with wakefulness gives way to N1, the first stage of sleep, which is defined by a low-voltage, mixed-frequency pattern. In healthy adults, sleep typically begins with NREM sleep. This stage is referred to as "deep" or "slow-wave" sleep.ĮEG recordings showing all three stages of typical NREM sleep. In stage N3, the deepest stage of NREM, EEGs reveal high-amplitude (large), low-frequency (slow) waves and spindles.
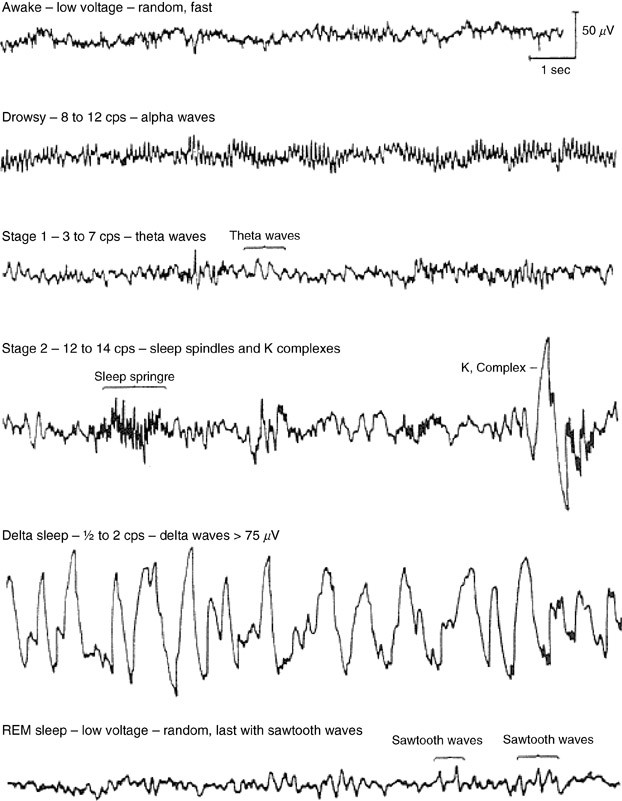
In the progression from stage N1 to N3, brain waves become slower and more synchronized, and the eyes remain still. NREM sleep can be broken down into three distinct stages: N1, N2, and N3. This is thought to be a neurological barrier that prevents us from "acting out" our dreams. Interestingly, during REM sleep muscles in the arms and legs are temporarily paralyzed. In contrast, people report dreaming far less frequently when awakened from NREM sleep. Typically, when people are awakened from REM sleep, they report that they had been dreaming, often extremely vivid and sometimes bizarre dreams. Many sleep experts think that these eye movements are in some way related to dreams. On an EEG, REM sleep, often called "active sleep," is identifiable by its characteristic low- amplitude (small), high-frequency (fast) waves and alpha rhythm, as well as the eye movements for which it is named. The two main types of sleep are rapid-eye-movement (REM) sleep and non-rapid-eye-movement (NREM) sleep.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
